Multimodal Human Intention Prediction
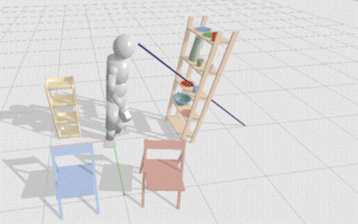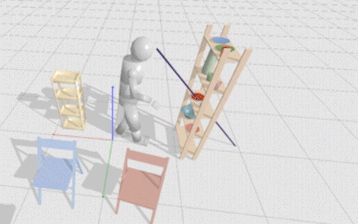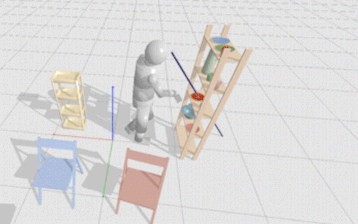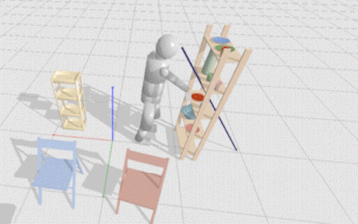
Description: Human intention prediction is an active area of research and has significant impact on a variety of applications including human-computer interaction, autonomous driving, as well as VR/AR applications. Plenty of works in cognitive science have revealed that human behaviours, e.g. human eye movements and human body movements, are correlated with intention objects. Therefore, it would be very interesting and meaningful to explore how to predict human intention from multimodal human behaviour features.
Goal: Evaluate and analyse the effectiveness of existing intention prediction methods. Develop deep learning methods to predict human intention from multimodal human behaviour features.
Supervisor: Zhiming Hu
Distribution: 70% Implementation, 10% Literature, 20% Analysis
Requirements: Good knowledge of deep learning, strong programming skills in Python and PyTorch. Preferable: knowledge of multimodal learning.
Literature: Kratzer, P., et al. 2020. MoGaze: A dataset of full-body motions that includes workspace geometry and eye-gaze. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 6(2), p.367-373.
Petković, T., et al. 2022. Ensemble of LSTMs and feature selection for human action prediction. International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems (ICIAS).
Belardinelli A, Kondapally A R, Ruiken D, et al. 2022. Intention estimation from gaze and motion features for human-robot shared-control object manipulation. arXiv:2208.08688.
Fuchs, S. and A. Belardinelli. 2021. Gaze-based intention estimation for shared autonomy in pick-and-place tasks. Frontiers in Neurorobotics 15.
David-John B, Peacock C, Zhang T, et al. 2021. Towards gaze-based prediction of the intent to interact in virtual reality, ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications (ETRA), p.1-7.

