Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation in the Wild
Xucong Zhang, Yusuke Sugano, Mario Fritz, Andreas Bulling
arXiv:1504.02863, pp. 1–10, 2015.
Abstract
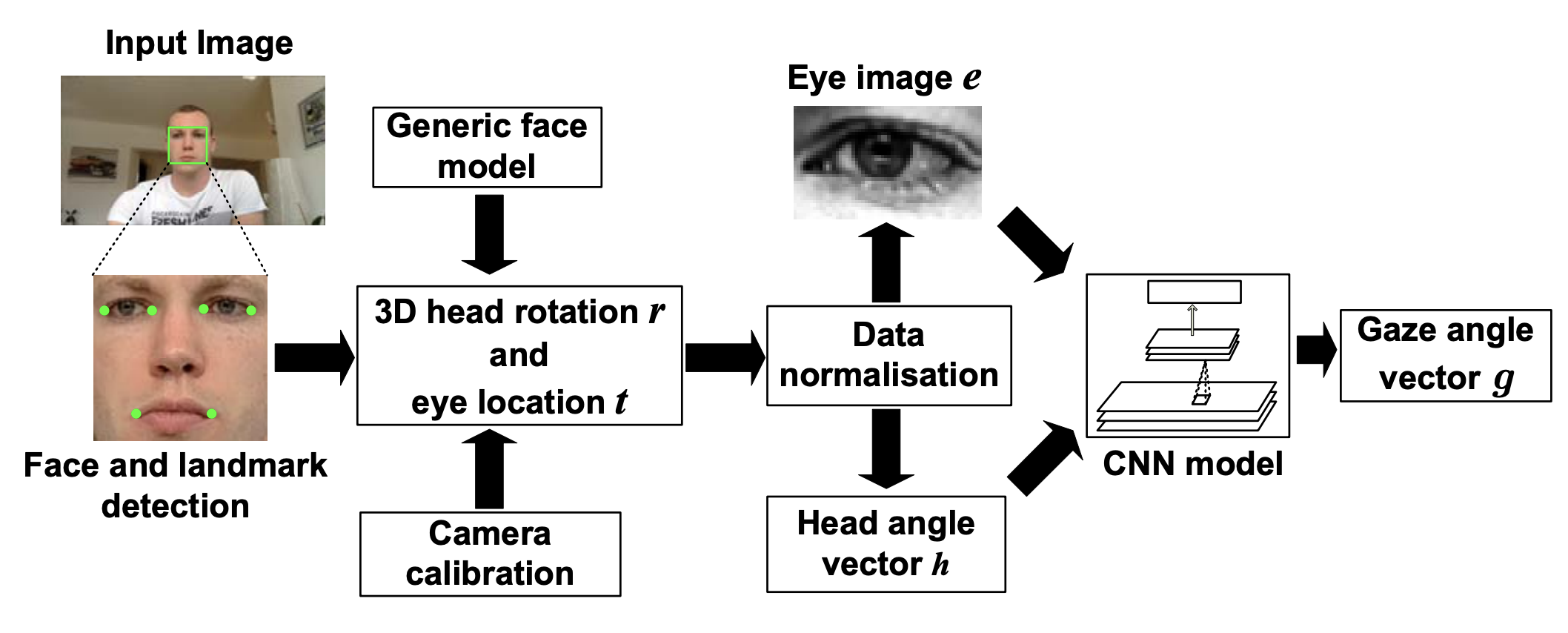
Appearance-based gaze estimation is believed to work well in real-world settings, but existing datasets have been collected under controlled laboratory conditions and methods have been not evaluated across multiple datasets. In this work we study appearance-based gaze estimation in the wild. We present the MPIIGaze dataset that contains 213,659 images we collected from 15 participants during natural everyday laptop use over more than three months. Our dataset is significantly more variable than existing ones with respect to appearance and illumination. We also present a method for in-the-wild appearance-based gaze estimation using multimodal convolutional neural networks that significantly outperforms state-of-the art methods in the most challenging cross-dataset evaluation. We present an extensive evaluation of several state-of-the-art image-based gaze estimation algorithms on three current datasets, including our own. This evaluation provides clear insights and allows us to identify key research challenges of gaze estimation in the wild.Links
Paper: zhang15_arxiv.pdf
Paper Access: https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.02863
BibTeX
@techreport{zhang15_arxiv,
title = {Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation in the Wild},
author = {Zhang, Xucong and Sugano, Yusuke and Fritz, Mario and Bulling, Andreas},
year = {2015},
pages = {1--10},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.02863}
}

